Stratified Random Sampling In Research Methodology | Suppose we wish to study computer use of educators in the hartford system. Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Assume we want the teaching level (elementary, middle school, and high school) in our sample to be. Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique see our article probability sampling if you do not know what probability sampling is. To stratify this sample, the researcher would then randomly select proportional amounts of people from each age group.
Sample problem shows how to choose between simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. How to choose a sampling technique for research. Sampling is a method that allows researchers to infer information about a population based on as with all probability sampling methods, simple random sampling allows the sampling error to be stratified sampling improves the accuracy and representativeness of the results by reducing. This is an effective sampling technique for studying there are many situations in which researchers would choose stratified random sampling over other types of sampling. In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations.
This entry first addresses some terminological considerations. Such sampling is called stratified random sampling. Because these factors interact in complex ways, the best sampling method is seldom obvious. For stratified random sampling, we get to choose the sample size for each stratum. Suppose we wish to study computer use of educators in the hartford system. Under these conditions, stratification generally produces more precise estimates of the population percents than estimates that would be found from a simple random sample. Second, it discusses two main components of random sampling: Stratified sampling is where the population is divided into strata (or subgroups) and a. While simple random sampling is used in stratified random sampling, the extra leeway in picking the sample sizes for each please be sure to answer the question. In a stratified random sample design, the units in the sampling frame are first divided into groups, called strata, and a separate srs is taken in each stratum to form the total sample. Sampling is a method that allows researchers to infer information about a population based on as with all probability sampling methods, simple random sampling allows the sampling error to be stratified sampling improves the accuracy and representativeness of the results by reducing. A simple random sample is then chosen from each strata separately and later all these samples are combine. See the function strata from the package sampling.
A simple random sample is then chosen from each strata separately and later all these samples are combine. Stratified random sampling differs from simple random sampling, which involves the random selection of data from an entire population, so each how stratified random sampling works. For stratified random sampling, we get to choose the sample size for each stratum. To stratify this sample, the researcher would then randomly select proportional amounts of people from each age group. Sample problem shows how to choose between simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.

This entry first addresses some terminological considerations. Provide details and share your research! An introduction to research methods. The function selects stratified simple random please be sure to answer the question. The sample size of each stratum in this technique is proportionate to the population size of the stratum when viewed against the entire population. Randomness and known probabilities of selection. Suppose we wish to study computer use of educators in the hartford system. The following random sampling techniques will be discussed: This means that the each stratum has the same sampling fraction. Say cities/town, urban villages and rural areas to be obtained separately. In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations. Stratified sampling works best when a heterogeneous population is split into fairly homogeneous groups. Stratification is often used in complex sample designs.
Suppose we wish to study computer use of educators in the hartford system. Such sampling is called stratified random sampling. This entry first addresses some terminological considerations. Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into subpopulations that may differ in important ways. Stratified random sampling differs from simple random sampling, which involves the random selection of data from an entire population, so each how stratified random sampling works.
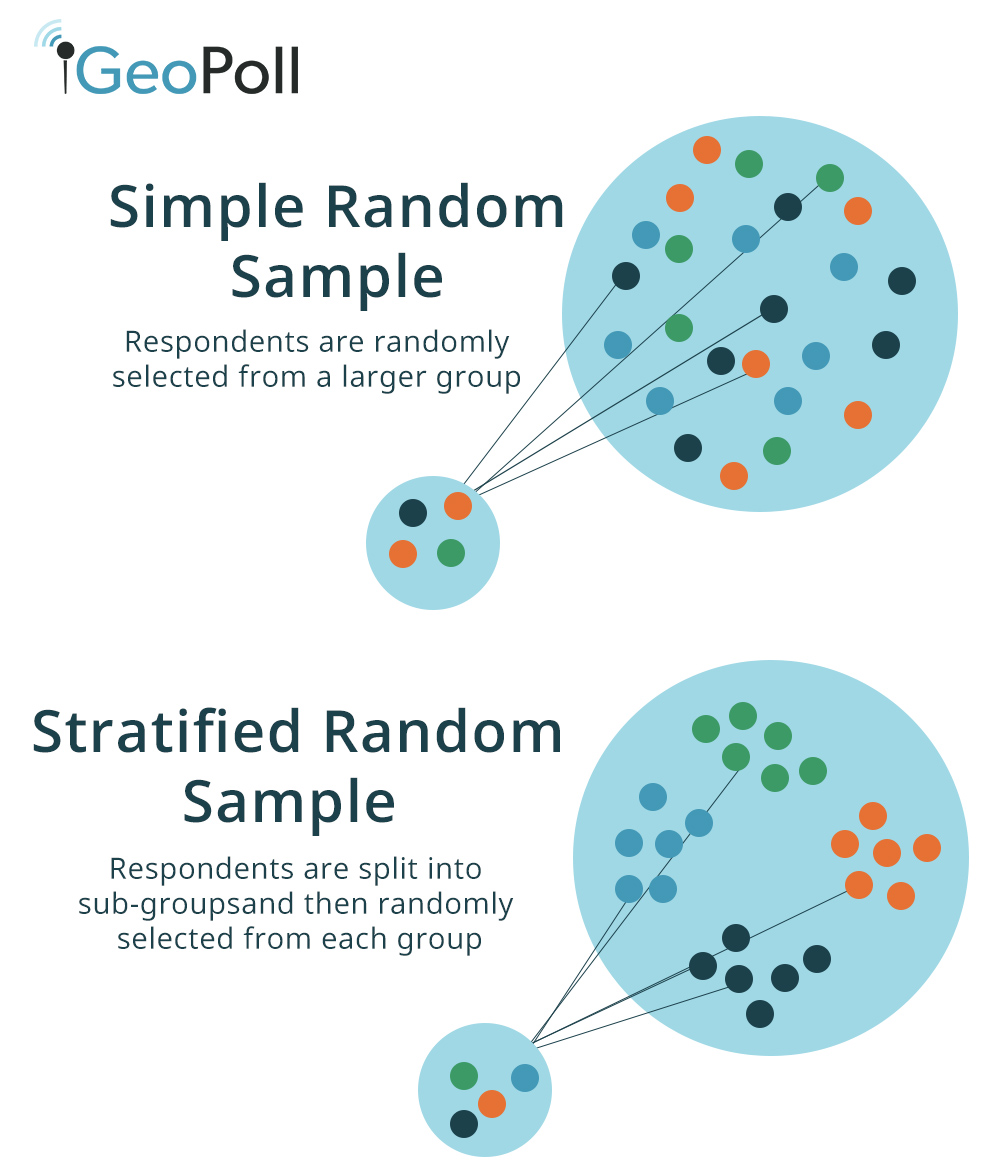
Stratified sampling is where the population is divided into strata (or subgroups) and a. Sample is easier than targeting unknown individuals. Random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling, systematic sampling, and convenience. The following random sampling techniques will be discussed: Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Provide details and share your research! The researcher identifies the different types of people that make up the target population and works out the proportions needed for the sample to be definitions summary table random sampling stratified sampling opportunity sampling systematic sampling sample size. Second, it discusses two main components of random sampling: In stratified random sampling the researcher divides the population into further subgroups called strata, this stratification can be on the basis of gender, districts, age, states or countries etc. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling method and a form of random sampling in which the population is divided into two or more groups (strata) according to one or more research process may take longer and prove to be more expensive due to the extra stage in the sampling procedure. Sample problem shows how to choose between simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Stratified sampling works best when a heterogeneous population is split into fairly homogeneous groups. An introduction to research methods.
Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into subpopulations that may differ in important ways random sampling in research. Assume we want the teaching level (elementary, middle school, and high school) in our sample to be.
Stratified Random Sampling In Research Methodology: Young the stratification may be proportionate or disproportionate.